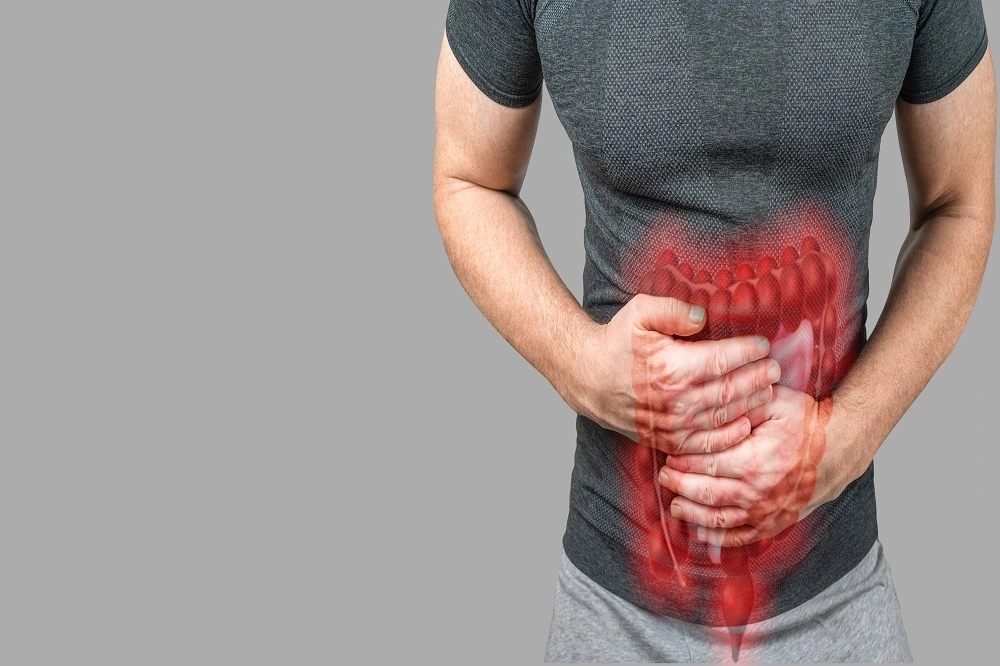
Celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten, affects millions worldwide. It leads to damage in your small intestine and interferes with the absorption of nutrients from food.
Here is everything you need to know to understand this condition, as well as what you can do to treat it.
What is celiac disease?
Celiac disease is a condition that affects your digestive system when you eat gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.
When you have this condition, consuming gluten triggers an immune response in your small intestine, leading to damage to the lining of your small intestine.
This damage hampers the absorption of nutrients, which can lead to various gastrointestinal and malabsorptive symptoms. Unlike a gluten intolerance or wheat allergy, celiac disease involves an immune response that can cause significant damage to the digestive tract over time.
The impact of celiac disease on the body
When you’re diagnosed with celiac disease, the impact on your body goes beyond just your digestive system. Consuming gluten triggers an immune response that damages the villi in your small intestine, which are critical for nutrient absorption. This damage leads to malnutrition, regardless of how much you eat, because your body can’t effectively absorb vitamins, minerals and other nutrients from your food.
Other related health issues include:
- Osteoporosis
- Infertility
- Neurological conditions
- Increased risk of certain types of cancer
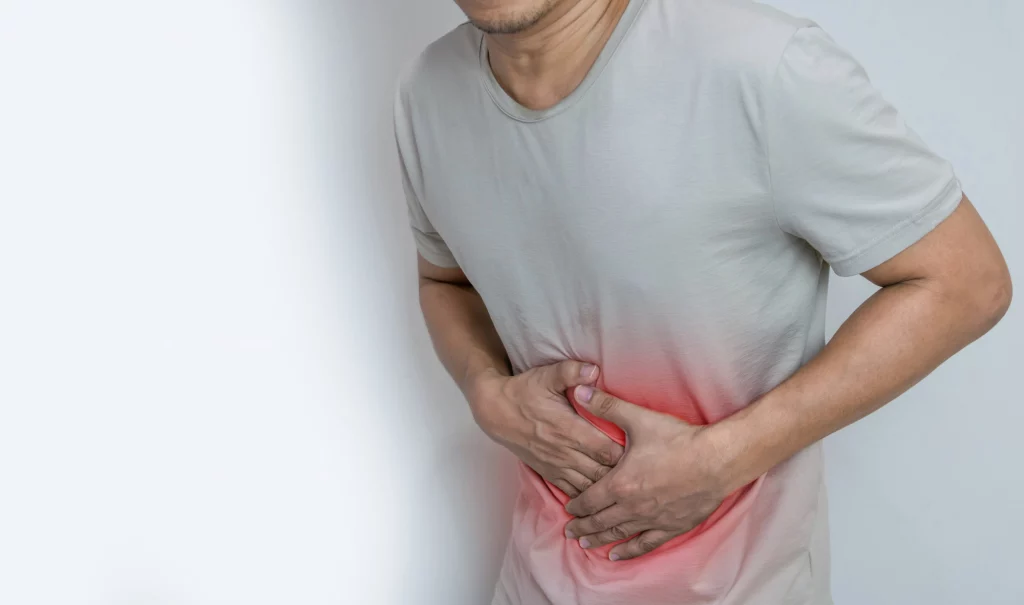
Recognizing the symptoms of celiac disease
Symptoms of celiac disease can vary significantly from person to person and may include digestive problems, which are common signs that your body is reacting adversely to gluten. These include:
-
- Bloating
- Diarrhoea
- Abdominal pain
The effects of celiac disease are not confined to the digestive tract. Other non-digestive symptoms include:
-
-
- Anaemia
- Loss of bone density
- Itchy skin rash
- Mouth ulcers
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
-
In children, the disease can manifest through:
-
-
- Irritability
- Delayed growth
- Failure to thrive
- Skin rashes (dermatitis herpetiformis)
- Poor weight gain
-
In some cases, you may have celiac disease with minimal or no digestive symptoms but still suffer from the long-term complications of the disease.
These symptoms can overlap with other conditions, which is why it’s important for you to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and to discuss potential celiac disease if you or your loved ones experience these symptoms.
Identifying the risk factors for celiac disease
When considering your risk for developing celiac disease, here are several factors that shape your susceptibility to this autoimmune disorder.
-
-
- Genetics. If you have family members, especially first-degree relatives like parents or siblings, diagnosed with celiac disease, your likelihood of having the condition increases. Besides family history, certain genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome and Turner syndrome, are linked with a higher incidence of celiac disease, pointing to a genetic connection in the disease’s occurrence.
- Genetic markers. Certain genetic markers (HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8) are associated with an increased risk, though not all carriers of these genes develop celiac disease.
- Having other autoimmune disorders. If you’re already managing autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes, autoimmune thyroid disease or autoimmune liver diseases, your body’s predisposition to develop additional autoimmune conditions, including celiac disease, is elevated.
- Gluten introduction. Timing and manner of gluten introduction to your diet as an infant also contributes to the risk of developing this disease.
-
Diagnosis and testing for celiac disease
Diagnosing celiac disease involves several steps, beginning with serologic (blood) tests to look for antibodies typically present in those with the disease. The most common tests include the tTG-IgA test and the EMA test.
If blood tests suggest celiac disease, an intestinal biopsy is often performed to confirm the diagnosis by examining the condition of the villi in your small intestine.
Genetic testing for HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 may also be used to rule out celiac disease.
Treatment approaches for celiac disease
The cornerstone of treating celiac disease is a strict, lifelong gluten-free diet.
This means eliminating all foods containing wheat, barley and rye from your diet, which are common sources of gluten. Adhering to this diet allows your small intestine to heal, alleviating symptoms and preventing further damage.
However, it’s not just about avoiding obvious gluten sources like bread and pasta. You must also be vigilant about hidden gluten in:
-
-
- Processed foods
- Sauces
- Medications
- Supplements
-
Reading labels becomes second nature as you learn to identify gluten-containing ingredients.
In addition to dietary changes, you may need supplements to correct nutritional deficiencies. Ongoing medical follow-up is important to monitor the healing of the intestine, nutritional status and compliance with the gluten-free diet.
Over time, you’ll discover a variety of gluten-free alternatives and learn to enjoy a wide range of foods without compromising your health. Education about the disease, reading food labels and learning how to avoid gluten while still maintaining a balanced diet are essential.
Key takeaway
Understanding celiac disease, from recognizing its symptoms to implementing effective treatment strategies, is important if you’re living with this autoimmune disorder.
Through strict adherence to a gluten-free diet and ongoing medical care, you can manage your symptoms and minimize the risk of complications, which can lead to a healthier and more fulfilling life.