If your throat feels sore, how’d you know if it’s caused by a virus or bacteria?
Knowing the difference between the two and how long the condition lasts can help you make informed decisions in seeking medical help.
In this article, we’ll explore the duration of strep throat, the importance of the rapid strep test, and what you need to know about managing this condition effectively.
What is strep throat?
Strep throat is a bacterial infection caused by the group A Streptococcus bacteria, specifically Streptococcus pyogenes.
It’s characterized by these symptoms:
- Severe sore throat
- Pain and difficulty swallowing
- Redness or swelling of the tonsils
Unlike most sore throats, which are viral in nature and resolve on their own within a week, strep throat requires antibiotic treatment to prevent complications and reduce the duration of symptoms.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), untreated strep throat can last for several weeks, with symptoms persisting for up to three weeks or longer. However, with appropriate antibiotic treatment, the duration of strep throat symptoms can be significantly reduced. It is important to note that antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections and are not useful for viral sore throats.
How is strep throat transmitted?
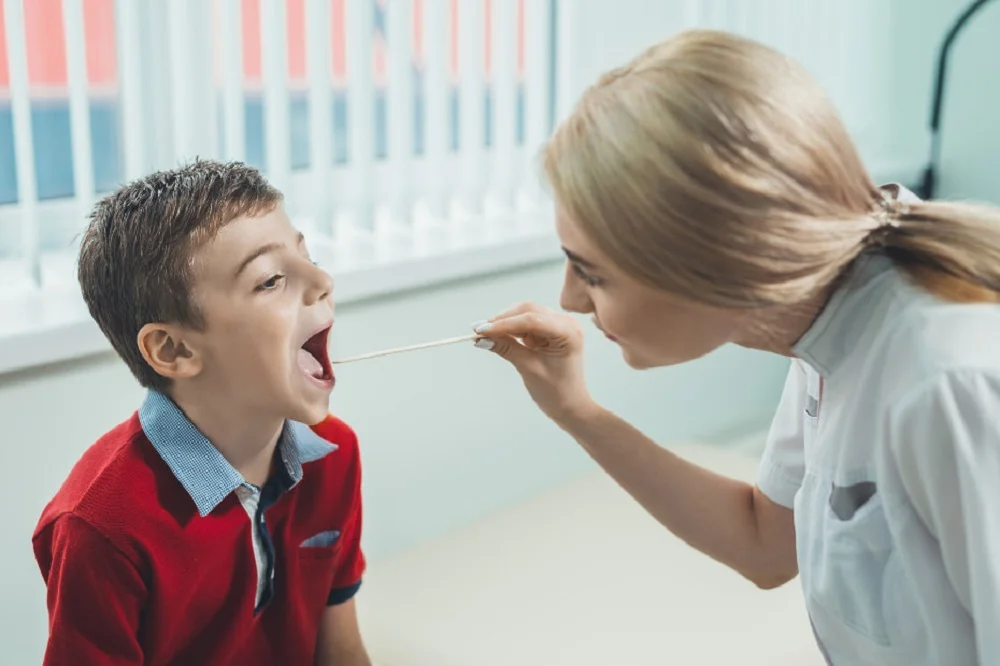

Strep throat is highly contagious and can be easily transmitted from person to person. The primary mode of transmission is through respiratory droplets when an infected individual coughs, sneezes or talks.
The streptococcus pyogenes bacteria responsible for strep throat can survive on surfaces and objects for a short period, allowing indirect transmission through contact with contaminated surfaces.
What does strep throat look like?
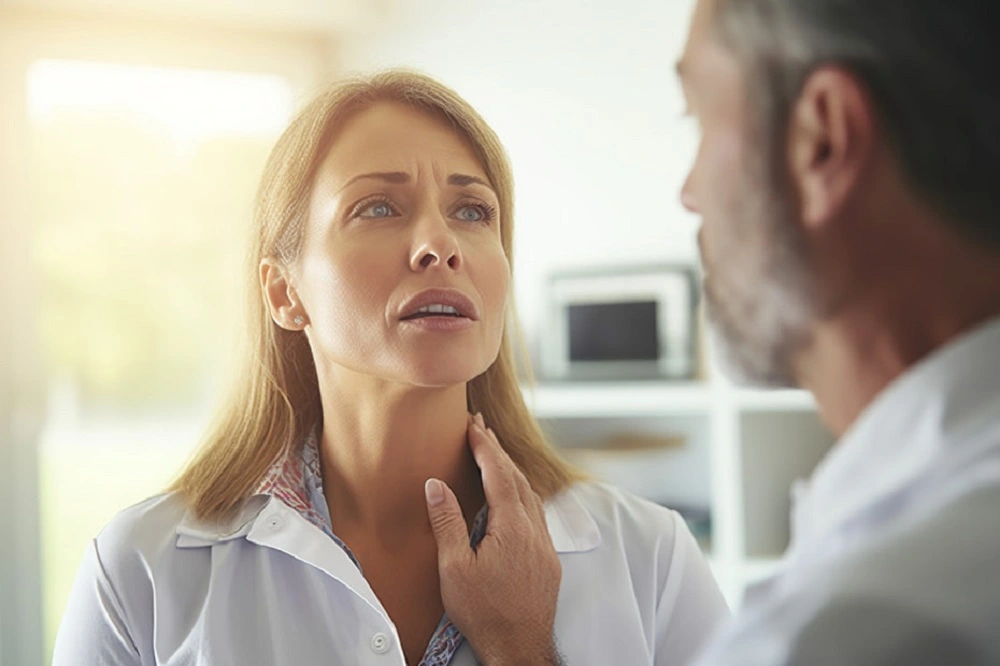

If you have a strep throat and you open your mouth, you may notice the following:
- Swollen tonsils with white or yellow spots
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Red and inflamed back of the throat
How is strep throat diagnosed?
If you’re experiencing a sore throat, it’s recommended to get tested as not all sore throats are caused by strep infections. Viral infections are more common and don’t require antibiotic treatment. A proper diagnosis allows you to proceed with the appropriate and timely treatment while preventing the transmission of the infection to others.
Strep throat is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. During a physical examination, your healthcare provider will assess symptoms.
To perform the test, they will take a throat swab and send the sample to a laboratory for analysis. Throat cultures may take a day or two until the results are released.
For faster testing, your healthcare provider can opt for a rapid strep test kit, which provides results within minutes.
How is strep throat treated?
Once strep bacteria are detected in your test, your healthcare provider will prescribe antibiotics to combat the infection and prevent complications.
Antibiotics help ease the symptoms, reduce the duration of the illness and minimize the risk of spreading the infection to others. They’re highly effective against bacterial infections but don’t work for viral infections, which are a common cause of sore throats. This is why it’s important to get diagnosed, so you’ll have the right medication for your condition.
How long does strep throat take to heal?

The duration of strep throat can vary, but with proper treatment, symptoms generally start to improve within one to three days. In general, you may feel significantly better within 48 hours of starting antibiotic treatment. Once you complete the full course of antibiotics, it’s highly likely that the bacteria have been eradicated and you can’t spread the virus to others.
If the symptoms persist or worsen beyond a week, consult with your healthcare provider as this may indicate an inadequate response to treatment or the presence of other underlying conditions. Prevention
Here are different ways that you can do to prevent contracting or spreading strep throat.
1. Practice good hygiene.
Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before eating or touching your face. Use hand sanitizer when soap and water are not readily available.
2. Avoid close contact.
Minimize close contact with people who have a confirmed or suspected case of strep throat. This includes refraining from sharing utensils, food or drinks with others.
3. Cover your mouth and nose.
When coughing or sneezing, use a tissue or your elbow to cover your mouth and nose to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets.
4. Disinfect frequently touched surfaces.
Clean and disinfect commonly touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, light switches and countertops, to reduce the presence of bacteria and viruses.
5. Strengthen your immune system.
A strong immune system can help reduce the risk of infections, including strep throat. Maintain a healthy lifestyle by doing the following:
- Getting enough sleep
- Eating a balanced diet
- Exercising regularly
- Managing stress
By following these preventive measures, you can lower the chances of contracting strep throat or spreading it to others.
When to see a doctor

It is advisable to see a doctor if you experience any of the following:
-
- Severe or persistent symptoms despite home remedies or over-the-counter medications
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Shortness of breath
- High fever (above 101°F or 38.3°C)
- Recurrent infections or complications
- Close contact with someone diagnosed with strep throat
If your child has suspected strep throat, they should be evaluated by a healthcare provider, as they may require specific treatment and monitoring to prevent potential complications.
Key takeaway
Strep throat is a common bacterial infection that primarily affects the throat and tonsils. It‘s important to differentiate strep throat from other types of sore throat as it requires specific antibiotic treatment to prevent complications and reduce the duration of symptoms. With proper medical care, including antibiotics, your strep throat symptoms typically improve within one to three days.