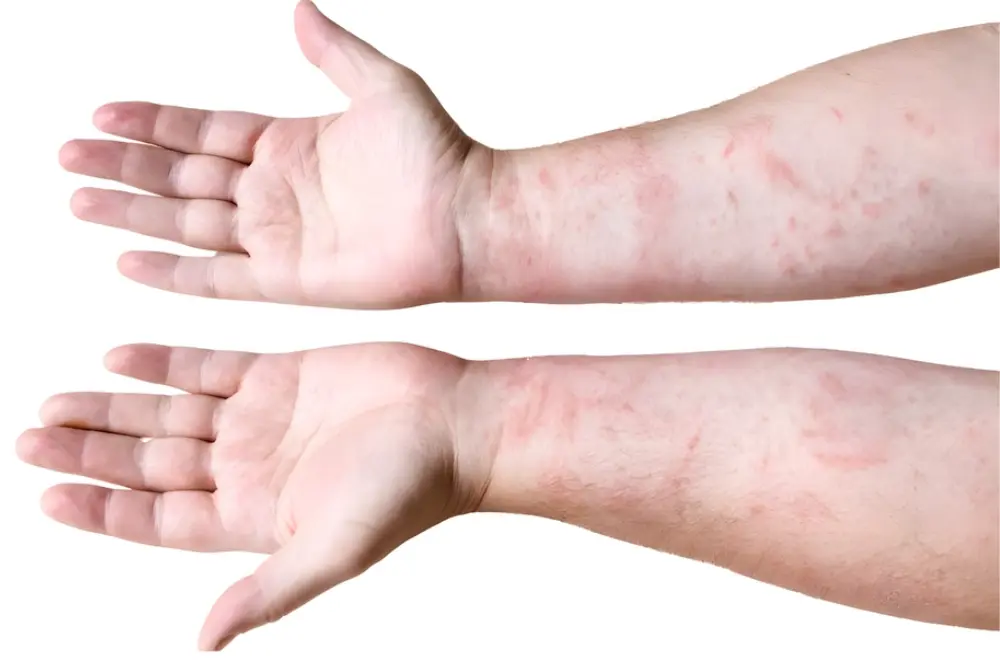
Secondary syphilis is a sneaky stage of the syphilis infection.
It can come with many symptoms as varied as they are unpleasant.
From rashes to fevers, hair loss, and fatigue, it’s a stage that’s hard to ignore, but you may not simply pinpoint.
What is secondary syphilis?
Secondary syphilis represents the second stage of the sexually transmitted infection (STI) syphilis, which is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum.
This stage typically manifests weeks to months after the initial infection, following the resolution of the primary stage’s hallmark symptom, which is a single sore or chancre. Without appropriate treatment, syphilis can progress to its latent and potentially most harmful stage—tertiary syphilis. At this stage, the infection can cause severe damage to your organs, such as the following:
- Heart
- Brain
- Nervous system
Is secondary syphilis curable?
Yes, secondary syphilis is curable with appropriate antibiotic treatment. The most effective cure that your healthcare provider is most likely to prescribe is penicillin, an antibiotic that has been proven to combat the Treponema pallidum bacterium responsible for syphilis.
If you’re allergic to penicillin, an alternative that your healthcare provider may prescribe is doxycycline.
Also, to confirm that the infection is eradicated, do follow-up blood tests and monitor the overall success of your treatment regimen.
What are the symptoms of secondary syphilis?
Secondary syphilis symptoms are diverse. Some of which you may experience include the following:
- Rash that may appear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Headaches
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
How is secondary syphilis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider can diagnose secondary syphilis with these methods:
- Blood tests to detect antibodies against the Treponema pallidum bacterium
- Physical examination of symptoms, especially the characteristic rash
- Darkfield microscopy to directly observe spirochetes, the causative bacteria, in samples from lesions
Prior to going to your healthcare provider, rapid tests for syphilis are also effective in diagnosing your infection status. For high-quality at-home syphilis tests, check out our shop here.
What are the potential complications of secondary syphilis if untreated?
If left untreated, secondary syphilis can lead to severe health issues, including the following:
- Neurological problems. One of these is meningitis, which can affect your brain and spinal cord.
- Cardiovascular problem. Aortitis, which is the inflammation of the aorta, is a heart problem associated with syphilis and can lead to kidney failure, stroke or heart attack.
- Ocular syphilis. This is another serious complication that can potentially result in blindness if you don’t address your condition promptly.
- Gummatous lesions. Untreated syphilis can damage your skin, bones and other organs.
How to prevent secondary syphilis?
The most effective way to prevent secondary syphilis is by practicing safe sex. Use condoms during all sexual activities to reduce the risk of transmitting or contracting syphilis.
Second, if you’re sexually active, regular STD screenings can help to detect the condition early so you can proceed with prompt treatment of primary syphilis before it can progress to more advanced stages.
If you know a sexual partner with syphilis, avoid sexual contact to stop the spread of the disease.
Frequently asked questions
Is secondary syphilis curable?
Yes, secondary syphilis can be effectively treated with antibiotics.
What are the treatment options for secondary syphilis?
The primary treatment for secondary syphilis involves the administration of penicillin. Penicillin is the most commonly used medication for this purpose as it can successfully cure the infection and prevent further progression of the disease.
If you’re allergic to penicillin, alternative antibiotics such as doxycycline or azithromycin may be used under medical supervision.
How long does treatment for secondary syphilis take?
The duration of treatment for secondary syphilis typically involves a single dose of intramuscular penicillin for most cases. However, the total duration may vary based on your health condition and response to treatment.
Can secondary syphilis recur after treatment?
After successful treatment, secondary syphilis does not usually recur. However, you can become reinfected if exposed again. Regular follow-up tests are recommended to ensure the infection has been fully eradicated.
What are the consequences of untreated secondary syphilis?
Untreated secondary syphilis can progress to more serious stages, which can lead to severe health complications such as damage to the nervous system, heart, brain and other organs. Worse, it can potentially result in death.
Key takeaway
Secondary syphilis is serious, but you can completely cure it with the right treatment. Early diagnosis and prompt use of antibiotics, especially penicillin, are key to eliminating the infection and stopping it from progressing to more severe stages. Stay proactive about your sexual health to avoid the severe complications that come with untreated syphilis.
Explore our at shop for reliable HIV/syphilis antibody testing kits.